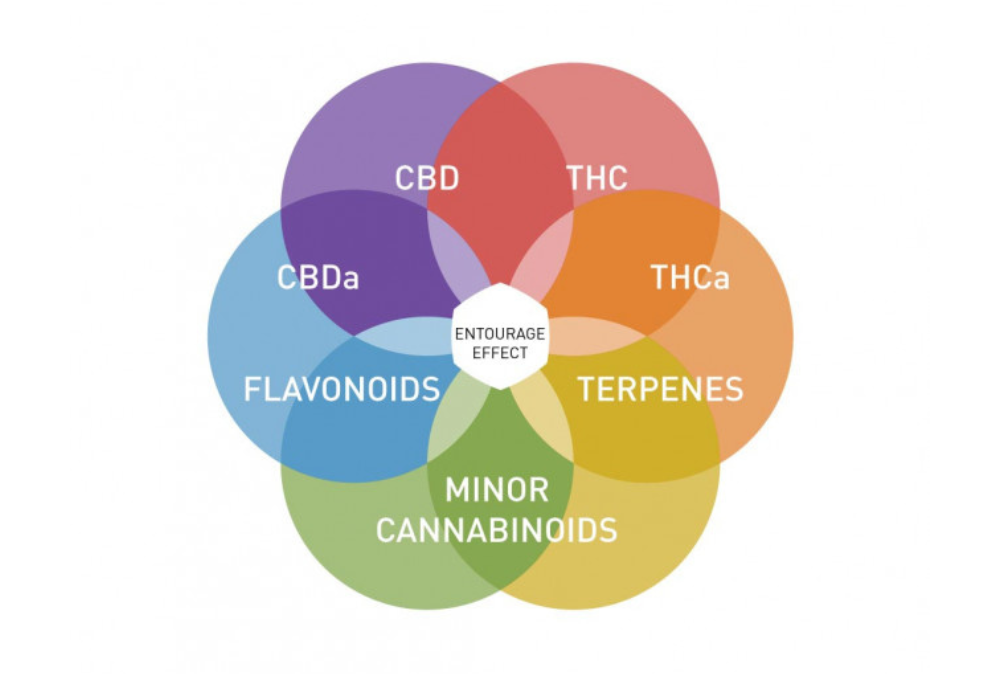
Cannabis is more than just THC and CBD. While these two cannabinoids are most widely recognized, the true therapeutic power of cannabis lies in how all of its components work together. We call this the entourage effect. Follow along as we dive into the entourage effect, how different compounds work together in whole plant medicine, and why it’s important for both medical and recreational cannabis users to understand.
The entourage effect is a term used to describe how the different compounds in cannabis — such as cannabinoids, terpenes, and flavonoids — work together to enhance or modify each other's effects. Instead of relying solely on one isolated cannabinoid, the entourage effect highlights how the whole plant, with all its naturally occurring compounds, provides a broader range of therapeutic effects than isolated compounds alone.
Cannabis contains hundreds of cannabinoids, each with unique effects. The most common include:
Each cannabinoid affects the body’s endocannabinoid system (ECS) differently, but when used together, they can produce more therapeutic benefits. This synergy is the key principle behind the entourage effect.
In addition to cannabinoids, terpenes play a significant role in the entourage effect. Terpenes are the aromatic compounds found in cannabis (and other plants) responsible for the smell and flavor. In addition, they also have their own therapeutic properties and interact with other compounds to enhance their effects.
For example:
When combined with cannabinoids, terpenes can modify how cannabis affects the body, further demonstrating the importance of using whole-plant medicine.
Whole-plant medicine uses cannabis in its natural, unaltered form, incorporating all cannabinoids, terpenes, and other compounds. Unlike isolated cannabinoid products (such as pure THC or CBD oils), whole-plant cannabis offers a more comprehensive therapeutic effect.
The benefits of whole-plant cannabis include:
Cannabinoids interact with the body’s endocannabinoid system (ECS), which regulates various physiological processes like pain, mood, and immune response. The ECS has two main types of receptors: CB1 and CB2. CB1 receptors are mainly found in the brain and central nervous system, while CB2 receptors are located in the peripheral nervous system and immune cells.
When cannabinoids like THC and CBD are consumed, they interact with these receptors to produce various effects. THC binds especially well to CB1 receptors, which causes the characteristic "high" sensation. On the other hand, CBD interacts more indirectly with both CB1 and CB2 receptors, potentially moderating the effects of THC.
The entourage effect occurs when multiple cannabinoids and terpenes work together to influence the ECS. For example, CBD can reduce the psychoactive effects of THC, making it easier for users to tolerate higher doses without feeling overly intoxicated. This interaction leads to a more balanced experience, both therapeutically and in terms of side effects.
To experience the full benefits of the entourage effect, it’s important to choose whole-plant cannabis products that provide a broad spectrum of cannabinoids and terpenes. Here’s what to look for:
The entourage effect underscores the importance of using whole-plant cannabis for therapeutic purposes. By understanding how cannabinoids, terpenes, and other compounds work together, users can maximize the therapeutic benefits of cannabis. Whether you're using cannabis for chronic pain, anxiety, or sleep issues, whole-plant cannabis offers a more balanced, holistic approach to wellness.
Embracing the entourage effect means tapping into the full potential of cannabis as a natural remedy. If you’re new to cannabis, start with full-spectrum products to experience the combined benefits of cannabinoids and terpenes. For more information on cannabinoids and the entourage effect, explore our website or schedule an appointment with one of our canna-expert QMPs.